6-July-2020
 |
| Mag Carbon Bricks |
Magnesia
carbon refractory bricks (MgO-C) or Carbon containing Magnesite refractories
have been extensively used by steel makers for the secondary treatment of steel
in basic oxygen furnaces, electric arc furnaces, and ladle furnaces. Mag Carbon
refractory bricks are widely used in slag lines of BOF (Basic Oxygen Furnace) because
of their superior wear resistance. The service life of Magnesia Carbon
refractories used in BOFs have been pushed quite significantly (largely due to
slag splashing and gunning improvements) even as the service conditions have
become more severe due to the increased operating temperature required for
continuous casting and the need to produce cleaner steel.
Mag Carbon
bricks are made of high purity magnesia, high quality graphite, antioxidants
and some additives with a suitable binder (bonding agent). Selection of raw
materials, their grading and grain size distribution (Granulometry) and
composition together have ultimate role in the development of various physical
properties, microstructure and ultimately thermo-mechanical properties of Mag Carbon
refractory bricks (MgO-C). Various different types of MgO (Magnesite) grains
provide different levels of corrosion resistance.
From
the literature and plant applications it has been established that
Magnesia-carbon bricks having 3 mm particle size show better wear resistance as
well as a few other characteristics as compared to the bricks with 5 mm size
grains.
Graphite, Anti-Oxidants
(Additives) and Binders used in the composition of Magnesia Carbon Bricks
The
graphite flakes used in these bricks impart -
=>
High thermal conductivity
=>
Good thermal shock resistance
=>
Low thermal expansion
=>
Non-wettability by liquid slag
=>
Low corrosion rates by slags
Graphite
contents of typical bricks range from 4 - 35% natural flake graphite. Since
oxygen affinity of carbon is very high so different kinds of antioxidant
minerals are used (in fines or superfines) in order to protect refractory
material against chemical corrosion. The REDOX reactions in magnesia carbon can
be reduced by selection of high purity magnesite, large crystal size and use of
graphite with low impurities. Slag corrosion resistance of MgO-C refractories
can be improved by use of magnesite grains with less reactivity i.e. fused
magnesite grains of high Bulk Density (BD) and high purity.
The
above are some of the reasons which explain how selection of various raw
materials can affect the performance of magnesia-carbon bricks. More on this
aspect and the compositions of Magnesia-carbon refractory bricks will be
discussed in a separate post:
Here,
our topic is Granulometry i.e. overall grading and the grain size distribution,
suitable for the best performance of MgO-C bricks. Grading and the grain size
distribution are important as these are directly related with the following
properties of Magnesia-carbon bricks:
=> Porosity
=>
Mechanical strength
=>
Spalling resistance
=>
Microstructure and phase development
=>
Wear resistance
From the
experience of various trials and performances it has been found that 0 - 4 mm
grading is the best for MgO-C refractory bricks for all general applications and
also for different shapes like Tap Hole Blocks, Sleeves, etc. (except Slide
Gate refractories which will be different).
Bonding
agents or binders used in Mag Carbon bricks and other carbon refractory
products are immiscible with graphite and other refractory raw materials. At
room temperature, they rely on binder to cure. Generally these binders or
bonding agents are resin, asphalt or an organic matter and can be divided into
three types: phenolic resin, modified asphalt, petroleum cracking by-product
category.
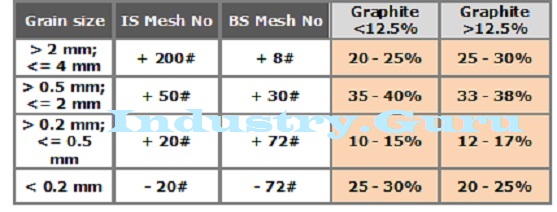
The grain
size distribution (granulometry) of the press mixture (powder) for MgO-C bricks
with different Graphite percentages as they should be are given in the
following table: